3.3.4 Monitoring
This section helps you configure sending of SNMP traps. Download the list of available traps, i.e. the MIB table, from the gateway web interface. The main purpose of SNMP monitoring is to observe your GSM gateway states continuously and send state information to the defined IP addresses whenever an error occurs. The SNMP agent on the CPU monitors the following states (some can be disabled by the user):
- GSM gateway accessibility;
- GSM/UMTS, PRI and VoIP card presence/absence;
- Count of active calls via PRI ISDN and VoIP;
- Received signal level for each GSM/UMTS module;
- ISDN line and GSM/UMTS module error states.
Refer to the List of SNMP traps for the list of all SNMP traps sent by 2N® StarGate.
Caution
- This service is subject to licence! Refer to Management / Licence key for the current GSM gateway licence state details.
Tip
- You can also apply ISDN monitoring to monitor the ISDN PRI line state. Refer to Gateway Configuration / ISDN Parameters – Monitoring for details.
Common Settings
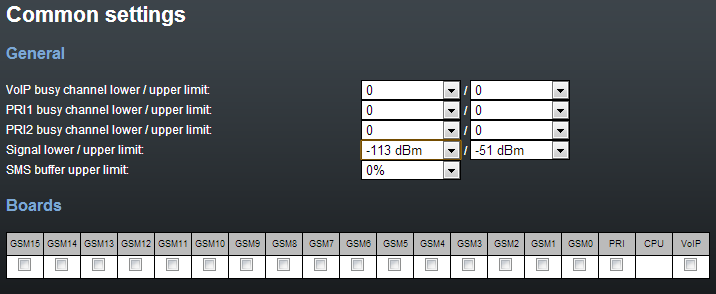
General
- Number of used channels – define the maximum/minimum count of active voice channels (VoIP, PRI ISDN). The SNMP trap is sent automatically whenever the defined values are exceeded.
- Signal level – define the maximum/minimum level of the signal received by the GSM/UMTS module. The SNMP trap is sent automatically whenever the defined values are exceeded.
- SMS buffer upper limit – define the maximum filling capacity of the SMS storage. The SNMP trap is sent automatically whenever the defined value is exceeded.
Boards
Enable/disable the card positions to be monitored. The CPU card is always monitored and monitoring cannot be disabled.
SNMP
General
Enabled – enable/disable the SNMP service.
Community – SNMP community is a group that owns the device and control stations on which SNMP is running. Default value = public.
Servers
- First SNMP server – the addressee's primary IP address and transport port for SNMP traps (default port = 162). Please make sure that the parameters have been completed correctly to avoid SNMP malfunction.
- Second SNMP server – the addressee's secondary IP address and transport port for SNMP traps (default port = 162). If these parameters are correctly completed, the SNMP traps will be sent both to the primary and secondary IP addresses.
Download MIB Files
This section helps you download the MIB files that are necessary for a proper function of your MIB browser.
Caution
The SNMP service works properly on condition that.
- SNMP is licensed in the Management section.
- The primary IP address, transport port and community parameters are completed.
- SNMP is enabled in the Monitoring section.