ISDN - Basic principle of VOIP operation and ISDN synchronization
This section describes the basic principle of VOIP operation for better understanding of Netstar SIP settings.
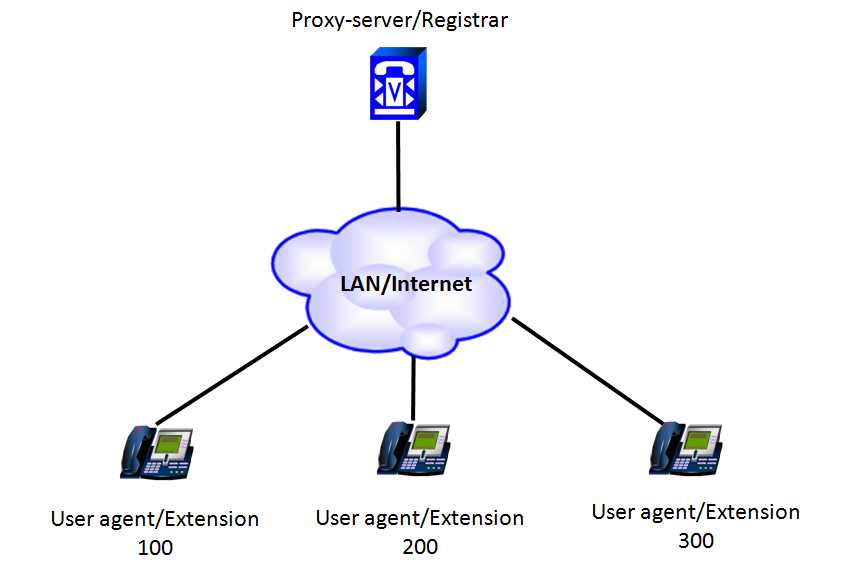
Netstar supports SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) only. Let us consider simplified network architecture of SIP:
Proxy server/Registrar is used to control all connections in the network. It monitors the state of User agents and their location according to IP address.
User agent is simple IP extension/phone. It must be registered on Proxy server/Registrar.
Each user agent periodically sends REGISTER messages to the Proxy server. The message contains user ID and its IP address.
Server replies with OK message. This message informs User agent that he is registered successfully and is able to make and receive the calls.
All signaling is managed by the Server. When connection is established User agents start sending/receiving voice packets using RTP (Reliable Transport Protocol).
All RTP packets are sent directly among User agents. Proxy server does not pass and process RTP packets, it is used only for signaling.
SIP messages have the format of HTTP protocol so the content of all messages can be captured and read in the network sniffer.
What should be set on Netstar to enable SIP communication?
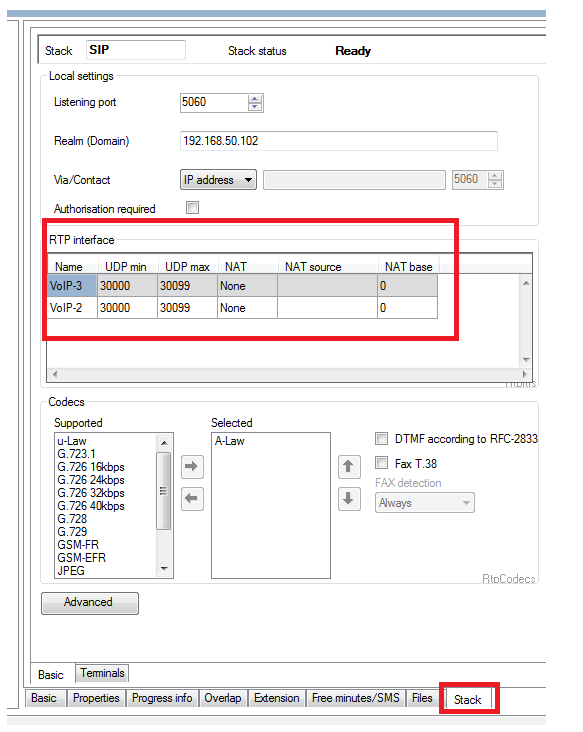
For SIP communication Netstar uses CPU and VOIP cards. CPU card has the functions of Proxy server/Registrar, it controls SIP signaling. VOIP card is used only for RTP packets processing.
Make sure that VOIP cards have assigned IP address. Otherwise the red LED will be shining on the front panel of VOIP card.
Also make sure that you selected proper VOIP card and port range for RTP processing:
Netstar supports DTMF transfer in the following modes:
- In-band (only for G.711 codec)
- RFC-2833
- SIP INFO (only receiving)
ISDN synchronization.
Hardware configuration of Netstar can have PRI or BRI ports. Netstar can be used in different scenarios. That is why it is very important to set ISDN synchronization.
Netstar can work in both modes: Master and Slave.
When Netstar is connected to PSTN, its port works as TE in Slave mode. All other ports which are connected to some PBX can be set as NT and Master.
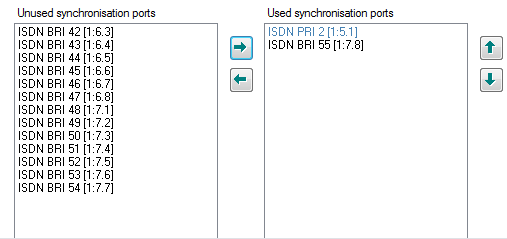
The ISDN port that receives a clock signal from PSTN can synchronize all other ISDN ports which are working as the Master. Netstar can have several sources of clock signal.
In this case it is necessary to set priority of the sources.
On the figure below the right side contains ISDN ports that receive clock signal and distribute it to the ports on the left side.