4.3.2 SIP 1 / SIP 2
2N® LiftIP 2.0 enables you to configure two independent SIP accounts (SIP1 and SIP2 folders). Thus, the device can be registered under two phone numbers, with two different SIP exchanges and so on. Both the SIP accounts process incoming calls equivalently. Outgoing calls are primarily processed by account SIP 1, or, if account SIP 1 is not registered (due to SIP exchange error, e.g.), by account SIP 2. Select the account number for the phone numbers included in the phone directory to specify the account to be used for outgoing calls (example: 2568/1 - calls to number 2568 go via account SIP 1, sip:1234@192.168.1.1 calls to sip uri via account SIP 2).
- SIP Account Enable – allow the SIP account use for calling. If disallowed, the account cannot be used for making outgoing calls and receiving incoming calls.
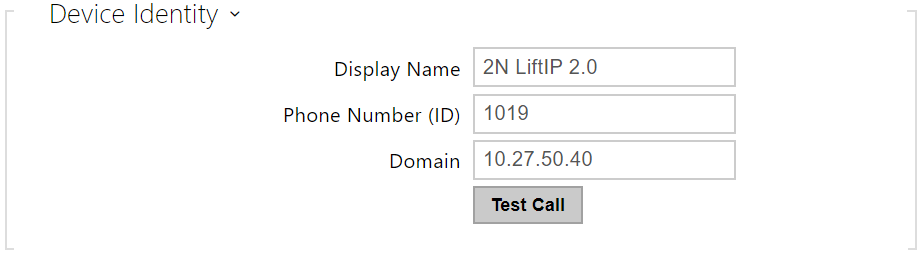
- Display Name – set the name to be displayed as CLIP on the called party's phone.
- Phone Number (ID) – set a device name (or another unique ID composed of characters and digits). Together with the domain, this number identifies the device uniquely in calls and registration.
- Domain – set the domain name of the service with which the device is registered. Typically, it matches the SIP Proxy / Registrar address.
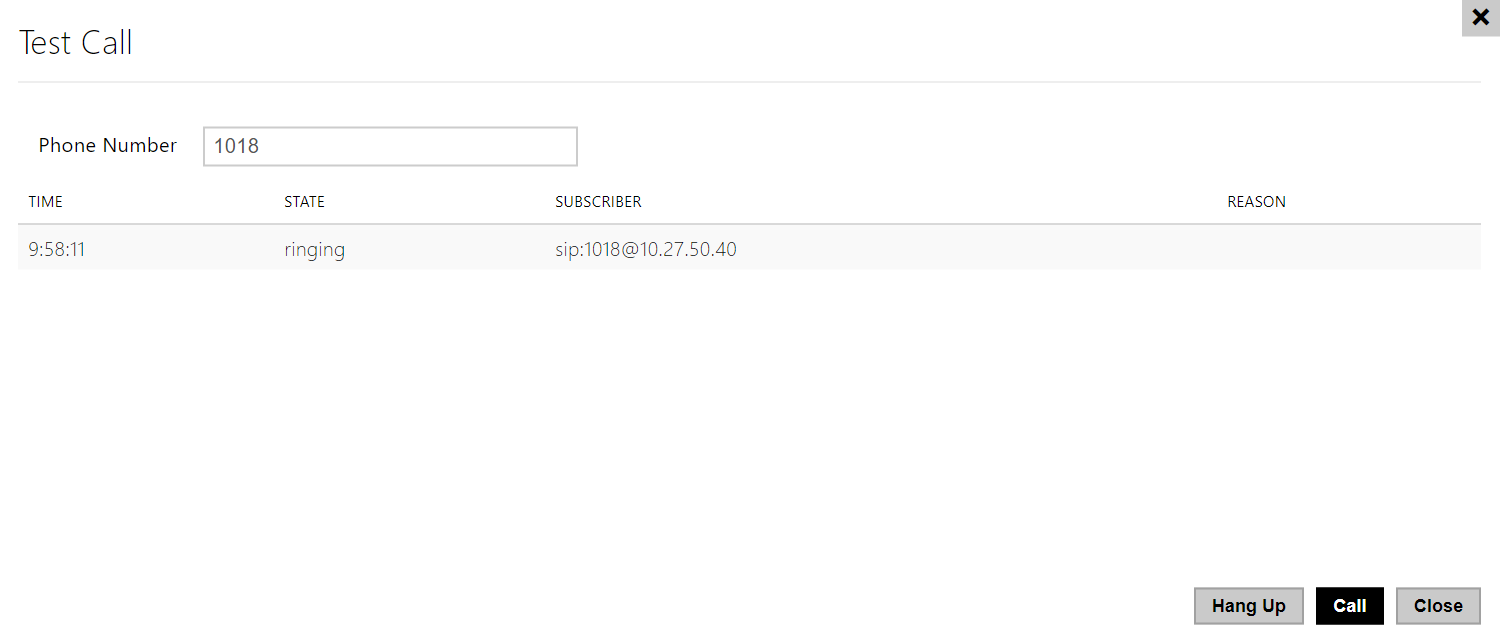
- Test Call – display a dialog box to make a test call to a selected phone number, see below.
- Authentication ID – set an alternative user ID for device authentication.
- Password – set a password for device authentication. If your PBX requires no authentication, the parameter will not be applied.
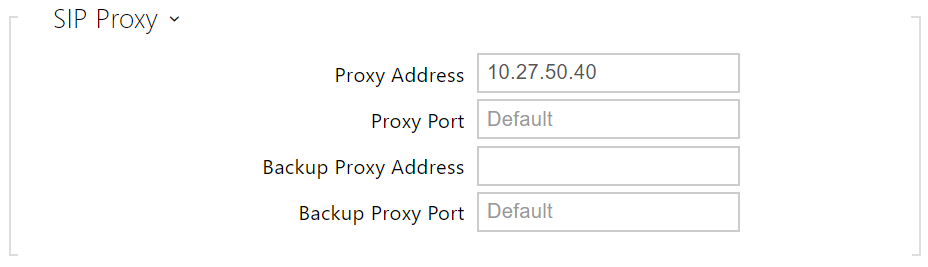
- Proxy Address – set the SIP Proxy IP address or domain name.
- Proxy Port – set the SIP Proxy port. The device uses the default port according to the transport layer (5060 or 5061) or the port obtained from the DNS in case the parameter is empty or set to 0.
- Backup Proxy Address – set the backup SIP Proxy IP address or domain name. The address is used where the main Proxy fails to respond to requests.
- Backup Proxy Port – set the backup SIP Proxy port. The device uses the default port according to the transport layer (5060 or 5061) or the port obtained from the DNS in case the parameter is empty or set to 0.
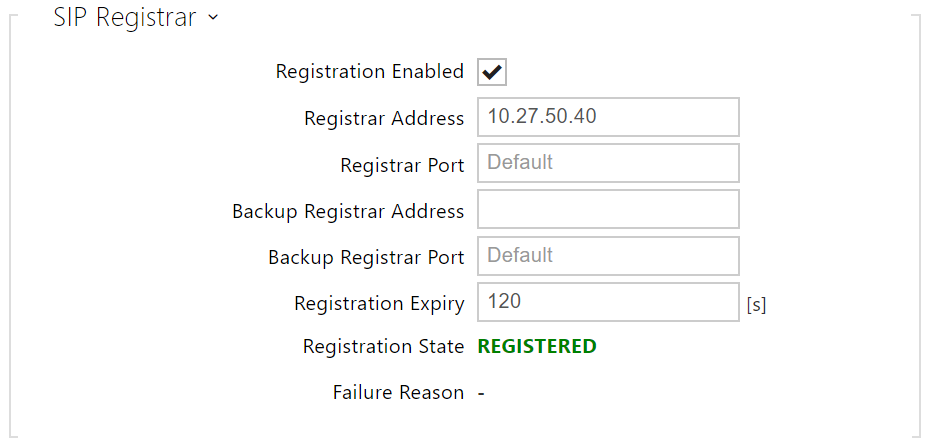
- Registration Enable – enable registration with the set SIP Registrar.
- Registrar Address – set the SIP Registrar IP address or domain name.
- Registrar Port – set the SIP Registrar port. The device uses the default port according to the transport layer (5060 or 5061) or the port obtained from the DNS in case the parameter is empty or set to 0.
- Backup Registrar Address – set the backup SIP Registrar IP address or domain name. The address is used where the main Registrar fails to respond to requests.
- Backup Registrar Port – set the backup SIP Registrar port. The device uses the default port according to the transport layer (5060 or 5061) or the port obtained from the DNS in case the parameter is empty or set to 0.
- Registration Expiry – set the registration expiry, which affects the network and SIP Registrar load by periodically sent registration requests. The SIP Registrar can alter the value without letting you know.
- Registration State – display the current registration state (Unregistered, Registering..., Registered, Unregistering...).
- Failure Reason – display the reason for the last registration attempt failure: the registrar’s last error reply, e.g. 404 Not Found.
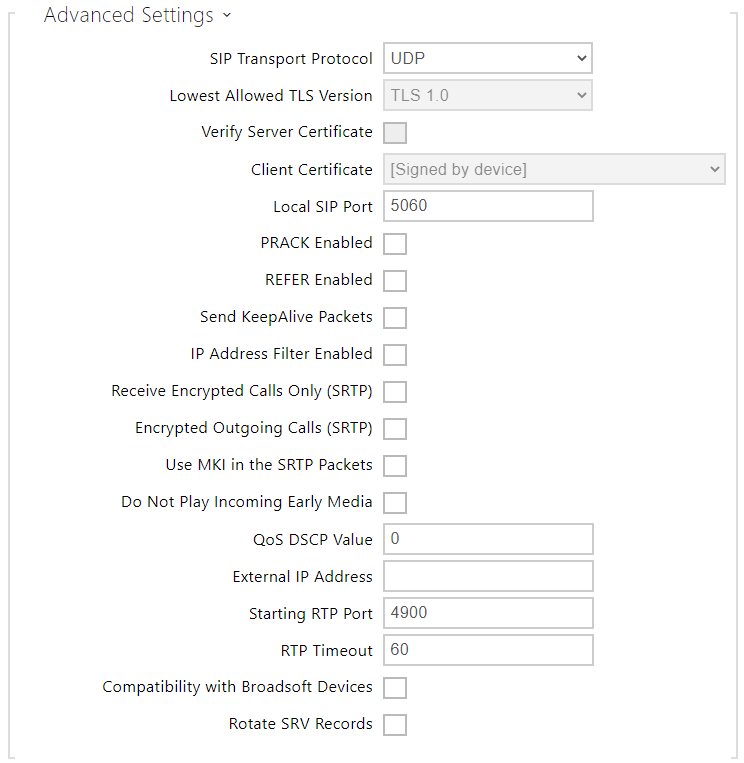
- SIP Transport Protocol – set the SIP communication protocol: UDP (default), TCP or TLS.
- Lowest Allowed TLS Version – set the lowest TLS version to be accepted for device connection.
- Verify Server Certificate – verify the SIP server certificate against the CA certificates uploaded to the device.
- Client Certificate – specification of the client certificate and private key used for verification of the device authorization to communicate with the SIP server.
- Local SIP Port – set the local port to be used for SIP signaling. A change of this parameter will not be applied until the device is restarted. The default value is 5060.
- PRACK Enabled – enable the PRACK method (reliable confirmation of SIP messages with codes 101–199).
- REFER Enabled – enable call forwarding via the REFER method.
- Send KeepAlive Packets – set whether or not the device shall periodically request the state of the called station via SIP OPTIONS (to detect any station failure during a call) during calls.
- IP Address Filter Enabled – enable blocking of SIP packets receiving from addresses other than SIP Proxy and SIP Registrar. The primary purpose of the function is to enhance communication security and eliminate unauthorized phone calls.
- Receive Encrypted Calls Only (SRTP) – set that SRTP encrypted calls shall only be received on this account. Unencrypted calls will be rejected. At the same time, TLS is recommended as the SIP transport protocol for higher security.
- Encrypted Outgoing Calls (SRTP) – set that outgoing calls shall be SRTP encrypted on this account. At the same time, TLS is recommended as the SIP transport protocol for higher security.
- Do Not Play Incoming Early Media – disable playing of the incoming audio stream before the call is answered (early media), which is sent by some PBXs or other devices. A standard local ringtone will be played instead.
- Use MKI in the SRTP Packets – enable the use of MKI (Master Key Identifier) if required by the counterparty for master key identification when multiple keys rotate in the SRTP packets.
- QoS DSCP Value – set the SIP packet priority in the network. The set value is sent in the TOS (Type of Service) field in the IP packet header. Enter the value as a decimal number. A change of this parameter will not be applied until the device is restarted.
- STUN Enable – enable STUN functionality for the SIP account. Address and ports acquired from the configured STUN server will be used in SIP headers and SDP media negotiation.
- STUN Server Address – set the IP address of the STUN server that will be used for this SIP account.
- STUN Server Port – set the port of the STUN server that will be used for this SIP account.
- External IP Address – set the public IP address or router name to which the device is connected. If the device IP address is public, leave this parameter empty.
- Starting RTP Port – set the starting local RTP port in the range of 64 ports to be used for audio and video transmissions. The default value is 4900 (i.e. the used range is 4900–4963). The parameter is only set for account 1 but applies to both the SIP accounts.
- RTP Timeout – set the timeout for receiving audio stream RTP packet during a call. If this limit is exceeded (RTP packets are not delivered), the call will be terminated by the device. Enter 0 to disable this parameter. The parameter is only set for account 1 but applies to both the SIP accounts.
- Compatibility with Broadsoft Devices – set compatibility with the Broadsoft PBXs. If, in this mode, the device receives re-invite from a PBX, it responds by repeating the last sent SDP with the currently used codecs instead of sending a complete offer.
- Rotate SRV Records – enable rotation of the SRV records for SIP Proxy and Registrar. This is an alternative method of transition to backup servers in the event of main server failure or unavailability.
Video
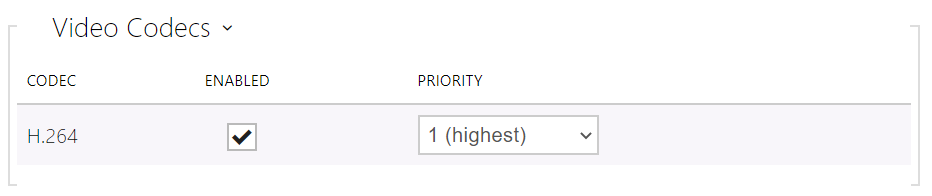
The chart helps you enable/disable the video codec H.264 offered for call setups and set its priority.
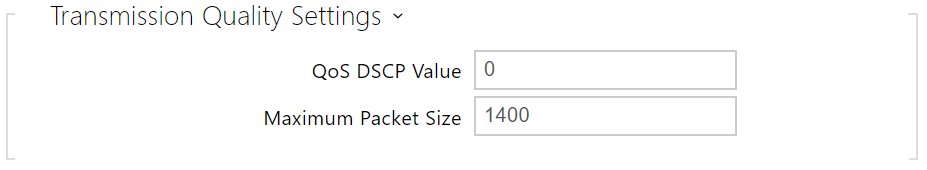
- QoS DSCP Value – set the video RTP packet priority in the network. The set value is sent in the TOS (Type of Service) field in the IP packet header.
- Maximum Packet Size – set the size limit for the video RTP packets to be sent.
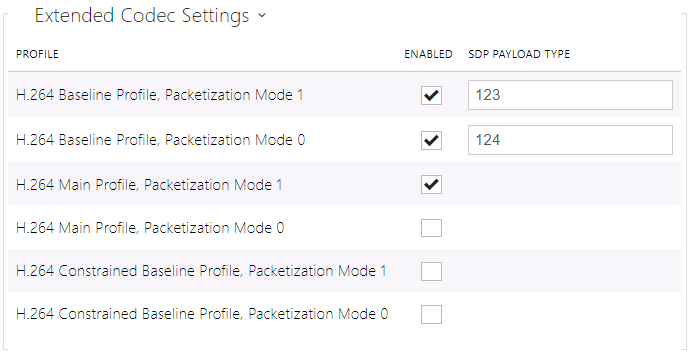
There can be different extended codec settings for different device types.
- H.264 Baseline Profile, Packetization Mode 1
- H.264 Baseline Profile, Packetization Mode 0
- H.264 Main Profile, Packetization Mode 1
- H.264 Main Profile, Packetization Mode 0
- H.264 Constrained Baseline Profile, Packetization Mode 1
- H.264 Constrained Baseline Profile, Packetization Mode 0
- Enabled – enable the packetization mode and set the payload type for each codec. The payload type can be selected automatically in case it cannot be set manually.
- SDP Payload Type – set the payload type for video codec H.264 (packetization mode 1). Set a value from the range of 96 through 127, or 0 to disable this codec option.
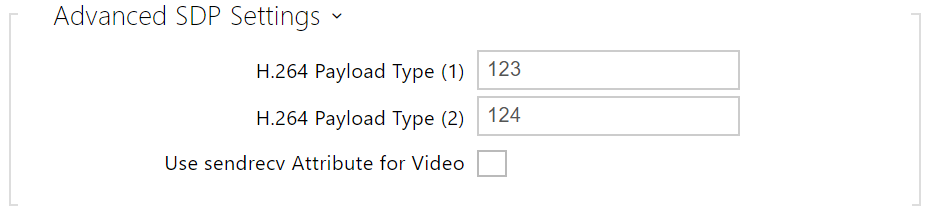
- H.264 Payload Type (1) – set the payload type for video codec H.264 (packetization mode 1). Set a value between 96 and 127 or 0 to disable this codec type.
- H.264 Payload Type (2) – set the payload type for video codec H.264 (packetization mode 2). Set a value between 96 and 127 or 0 to disable this codec type.
- Use sendrecv Attribute for Video – the setting used to be called Compatibility with Polycom phones. It helps ensure compatibility with some third party devices (Polycom/Cisco and others). With this mode enabled, the device sends sendrecv instead of sendonly in its SDP message in the video codec offer.
Audio
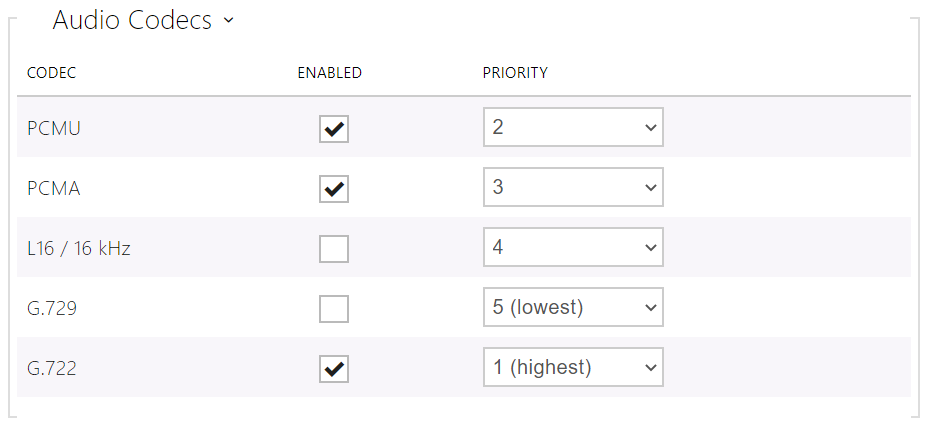
This chart helps you enable/disable the audio codecs offered for call setups and set their priorities.
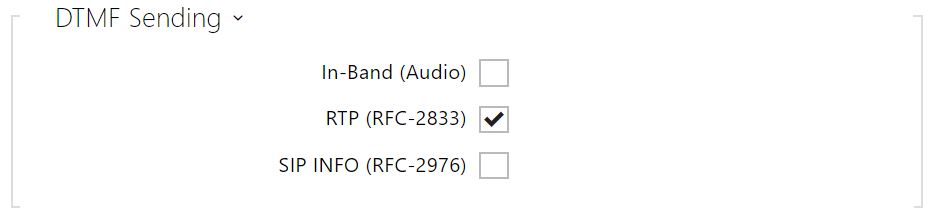
Sending DTMF helps you set the method of sending DTMF characters from the device. Check the opponent’s DTMF receiving options and settings to make the function work properly.
- In-Band (Audio) – enable the classic method of sending DTMF in the audio band using standardized dual tones.
- RTP (RFC-2833) – enable DTMF sending via the RTP according to RFC-2833.
- SIP INFO (RFC-2976) – enable DTMF sending via SIP INFO messages according to RFC-2976.
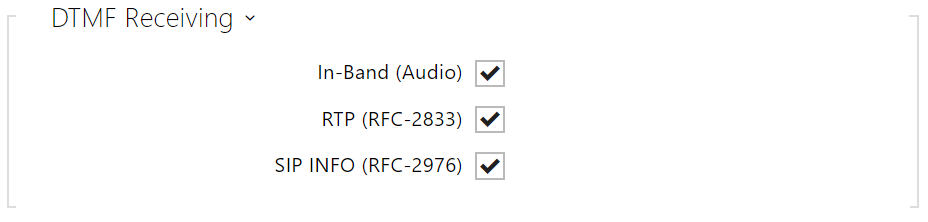
Receiving DTMF helps you set the method od receiving DTMF characters from the device. Check the opponent’s DTMF sending options and settings to make the function work properly.
- In-Band (Audio) – enable classic DTMF dual tone receiving in the audio band.
- RTP (RFC-2833) – enable DTMF receiving via RTP according to RFC-2833.
- SIP INFO (RFC-2976) – enable DTMF receiving via SIP INFO messages according to RFC-2976.
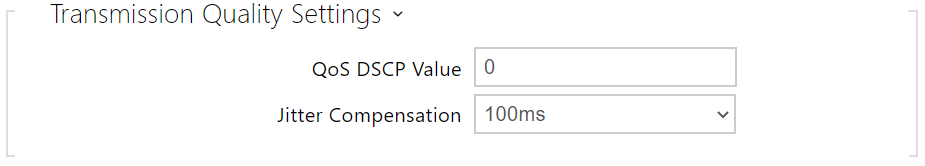
- QoS DSCP Value – set the audio RTP packet priority in the network. The set value is sent in the TOS (Type of Service) field in the IP packet header. Enter the value as a decimal number. A change of this parameter will not be applied until the device is restarted.
- Jitter Compensation – set the buffer length for compensation of interval unevenness in audio packet arrivals. Set a higher value to increase the receiving immunity at the cost of a higher sound delay.