3.1.3 VoIP
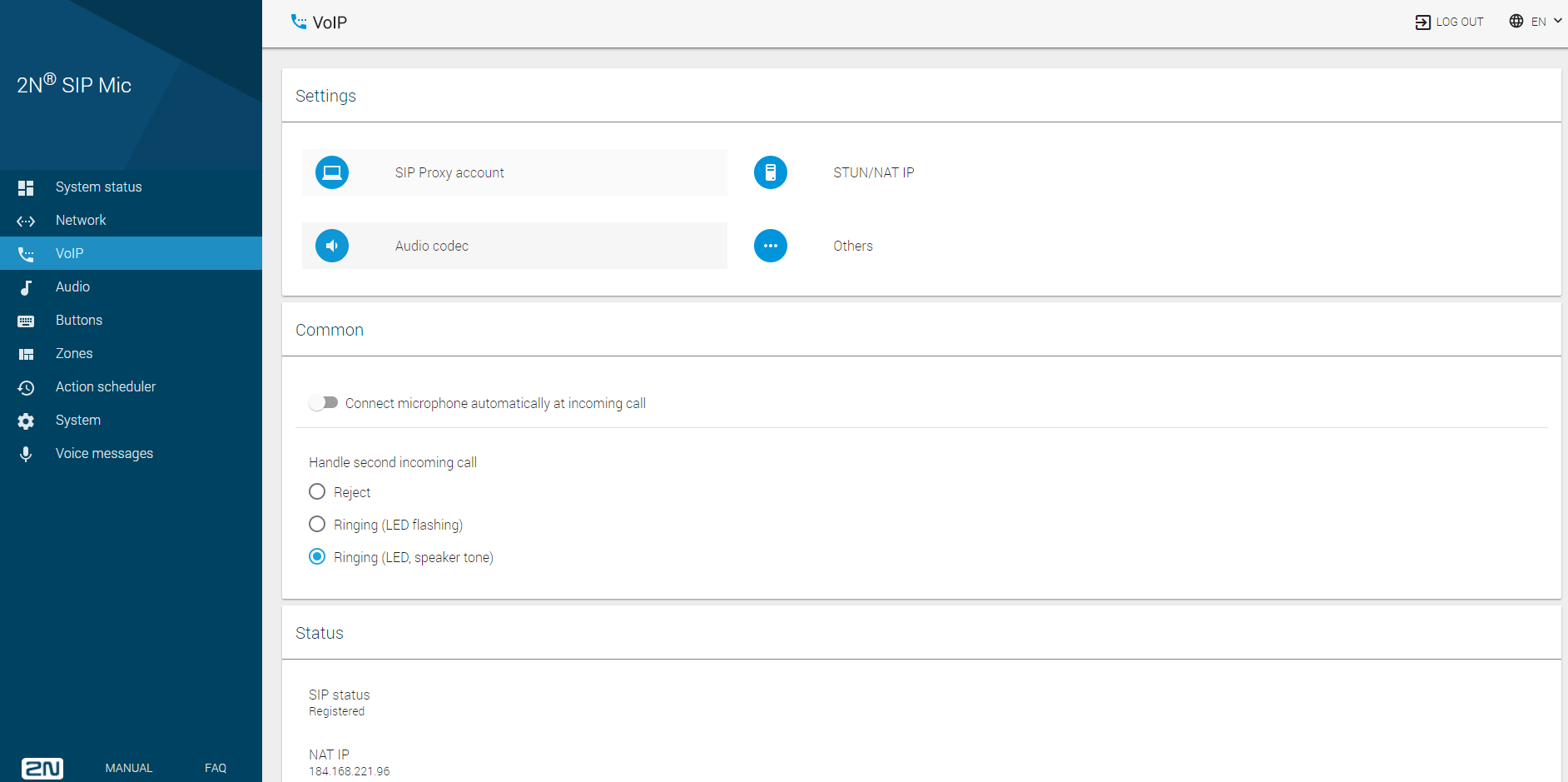
There are three SIP telephony sections in this menu. Use the Settings to set relevant call setup parameters, Proxy and registration server addresses, codec parameters and priorities and special actions during calls. Common helps you define how the device should receive calls or deal another incoming call. The Status section is for information only.
Settings
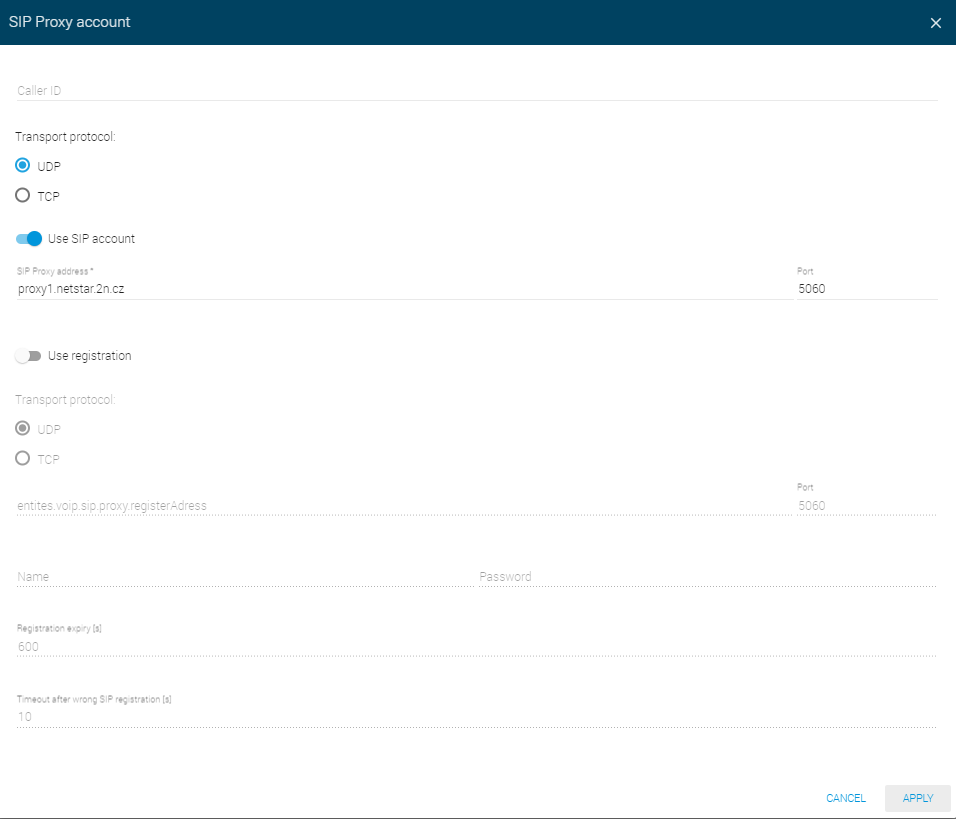
SIP Proxy account – set the user account parameters on the SIP Proxy Server: registration, protocols and registration expiry.
- Caller ID – set your own phone number (or another unique ID consisting of characters and digits), which, together with the domain, identifies 2N® SIP Mic in calls and registration.
- Transport protocol – specify whether the UDP or TCP should be strictly used for SIP and RTP transmission.
- Use SIP account – allow the SIP Proxy use.
- SIP Proxy address* – enter the opponent IP address or DNS (operator, PBX) to which 2N® SIP Mic should connect for call direction.
- Port – set the SIP Proxy listening port (typically 5060).
- Use registration – allow registration with the opponent and specify the phone number for registration (Caller ID). If the device is not registered, no call setup requests can be set to it.
- Transport protocol – choose UDP or TCP for SIP communication.
- Registration server IP address – set the opponent IP address (operator, PBX) to which 2N® SIP Mic should connect for registration requests.
- Port – set the SIP Registrar server listening port (typically 5060).
- Name – set the user name for 2N® SIP Mic authentication.
- Password – set the password for 2N® SIP Mic authentication. If your IP PBX does not request authentication, the parameter is not applied.
- Registration expiry – set the registration expiry to control the registration request load of your network and SIP Registrar. The SIP Registrar can modify the expiry without letting you know.
- Timeout after wrong SIP registration – set the timeout for the 2N® SIP Mic to register after an unsuccessful registration attempt.
STUN/NAT IP – STUN server helps NAT clients (i.e. the PCs behind the firewall) set up phone calls to the VoIP hosted outside the LAN.
- Use local IP – use the local device IP address.
- STUN
- STUN server – enter the STUN server address (IP or domain name). The address is used if STUN IP is selected in the RTP interface configuration.
- Port – set the port to be used for STUN. The default value is port 3478.
- STUN, keep alive
- STUN server – enter the STUN server address (IP or domain name). The address is used if STUN IP is selected in the RTP interface configuration..
- Port – set the port to be used for STUN. The default value is port 3478.
- Refresh rate – define the keep-alive packet sending period. The default value is 600 s.
- NAT IP – enter the public IP address and NAT port to which signalling messages shall be sent by the opponent. Packets are then sent to the PBX as defined in the port routing and router IP address settings.
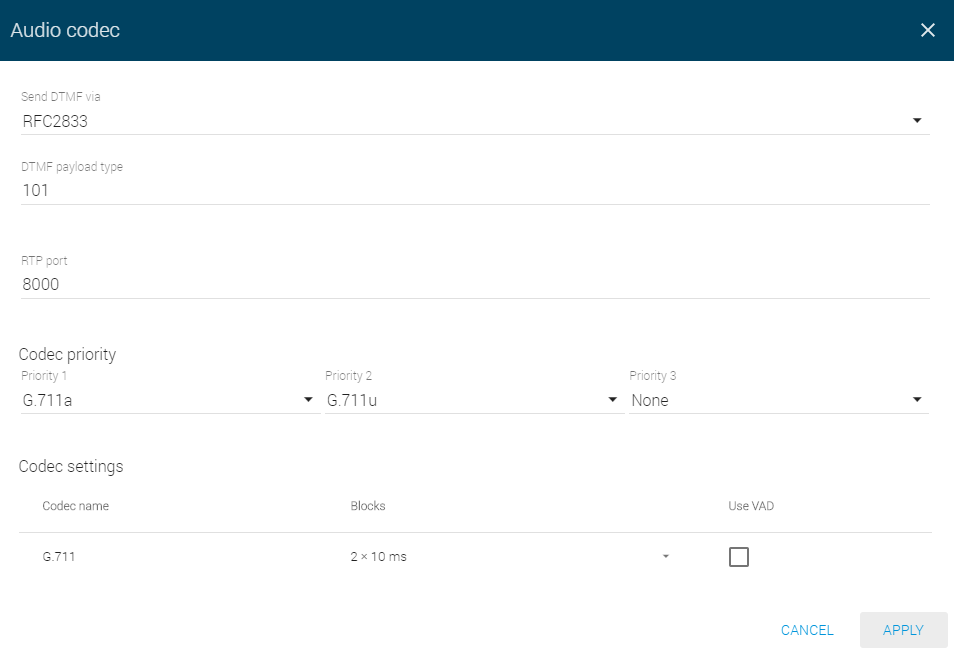
Audio codec
- Send DTMF via – choose the DTMF sending type.
- Inband (Audio) – allow the classic DTMF sending in the audio band using standardised dual tones.
- RFC2833 – allow DTMF sending via RTP according to RFC-2833.
- SIP info – allow DTMF sending via SIP INFO messages according to RFC-2976.
- DTMF payload type – set the payload type for DTMF: any value from 96 to 127. Make sure that the Proxy and end terminals are identical to make the function work properly.
- RTP port – set the local RTP port to be the source of the RTP stream sent from the device.
- Codec priority – enable/disable the use of audio codecs offered at the call setup and set the priority. The options are G.711a (alaw), G.711u (ulaw) and G.722.
- Codec settings – set the codec specific parameters.
- Codec name
- Blocks – set the size of the data block to be sent. Used for more effective use of the bandwidth.
- Use VAD – use VAD for data transmission optimisation. Packets are not sent when the user is not speaking. VAD stands for Voice Activity Detector.
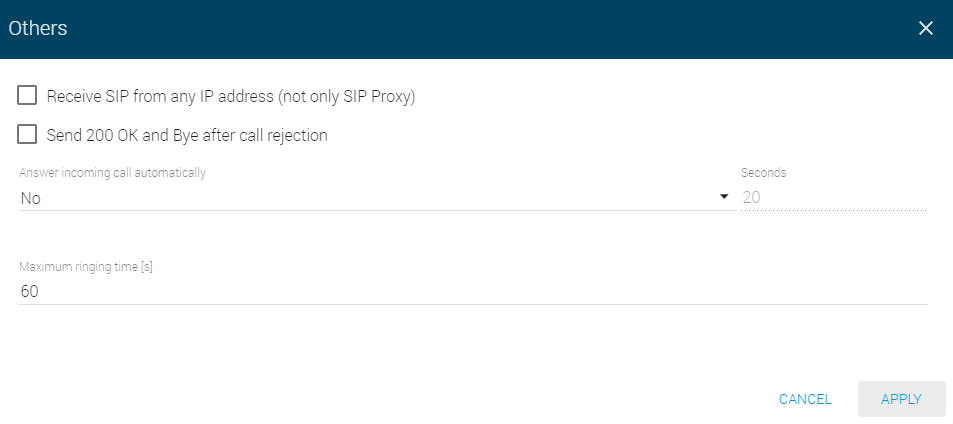
Others
- Receive SIP from any IP address (not only from SIP Proxy) – select receiving SIP messages from addresses other than SIP Proxy. Used for direct calling to an IP address, for example.
- Send 200 OK and Bye after call rejection – allow sending 200 OK and BYE messages after call rejection. It is a specific setting. The call is then identified as received and immediately terminated on the Proxy. Normally, the call is rejected with cause "404 Not Found".
- Answer incoming call automatically – set the 2N® SIP Mic incoming call answer type:
- No – 2N® SIP Mic does not answer incoming calls automatically. Receive the call manually.
- Yes – 2N® SIP Mic answer incoming calls immediately automatically.
- For x seconds – 2N® SIP Mic receives incoming calls in x seconds automatically. Set a value in the range of 1–3600. The maximum ringing time is not applied in this case.
- Maximum ringing time – set the maximum call setup and ringing time in which outgoing calls are terminated automatically. Set a value in the range of 1–3600. This parameter is applied only if the preceding parameter is set to No.
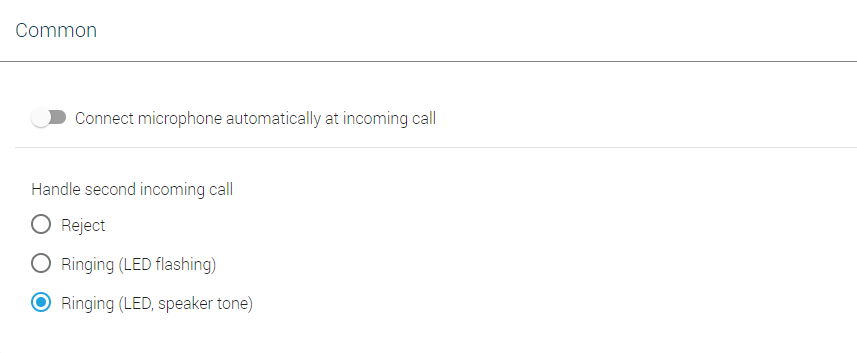
Common
- Connect microphone automatically at incoming call – this parameter is applied only if automatic call answering is selected (VoIP / Settings / Others menu). If you answer calls manually, it is not applied.
- Handle second incoming call – set how to handle a call that comes in while another call is active. The default value is Reject.
- Reject – the other incoming call is rejected.
- Ringing (LED flashing) – the other incoming call is signalled by flashing LEDs but does not affect the currently made call.
- Ringing (LED, speaker tone) – the other incoming call is signalled by flashing LEDs and ringing tone from the speaker. The ringing tone of the other call is different from the common ringing tone.
Note
- 2N® SIP Mic is capable of serving up to two calls at the same time. The third and next incoming calls are rejected.
Status
- SIP status – display the current SIP Proxy line status: Inactive, Active, Registered, Registration in progress and Registration error. Refer to the System Status subsection for details.
- NAT IP – display the set IP address for NAT if used. 0.0.0.0 is displayed when STUN server or Local IP is used.