5.6.1 Network
As the 2N IP intercom is connected to the LAN, make sure that its IP address has been set correctly or obtained from the LAN DHCP server. Configure the IP address and DHCP in the Network subsection.
Tip
- To know the current IP address of your intercom, use the 2N IP Utility, which can be freely downloaded from 2N.com, or apply the steps described in the Installation Manual of the respective intercom: the intercom communicates its IP address to you via a voice function.
If you use the RADIUS server and 802.1x-based verification of connected equipment, you can make the intercom use the EAP-MD5 or EAP-TLS authentication. Set this function in the 802.1x tab.
The Trace tab helps you launch capture of incoming and outgoing packets on the intercom network interface. The file with captured packets can be downloaded for Wireshark processing, e.g. (www.wireshark.org).
List of Parameters
Network
Basic
- Use DHCP Server – enable automatic obtaining of the IP address from the LAN DHCP server. If the DHCP server is unavailable or inaccessible in your LAN, use the manual network settings.
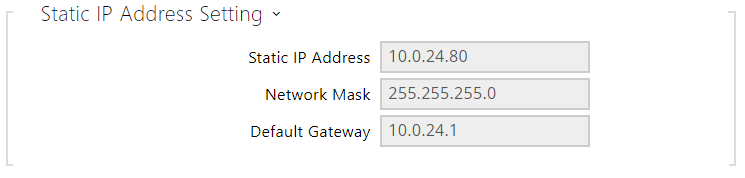
- Static IP Address – static IP address of the intercom, which is used together with the below mentioned parameters if the Use DHCP Server parameter is disabled.
- Network Mask – network mask.
- Default Gateway – address of the default gateway, which provides communication with off-LAN equipment.
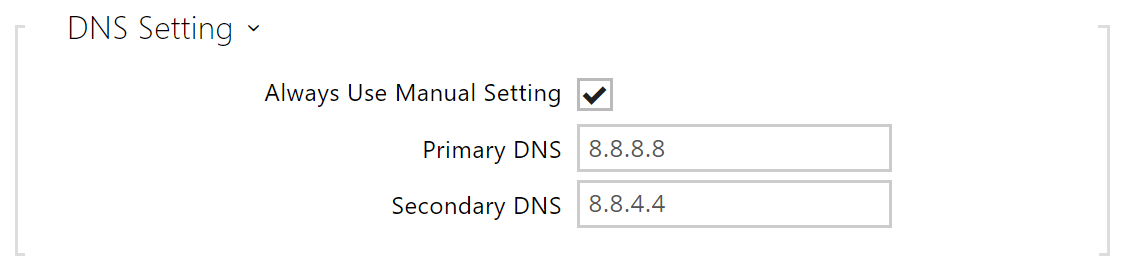
- Primary DNS – primary DNS server address for translation of domain names to IP addresses. The primary DNS value is 8.8.8.8 upon factory reset.
- Secondary DNS – secondary DNS server address to be used in case the primary DNS is inaccessible. The secondary DNS value is 8.8.4.4 upon factory reset.
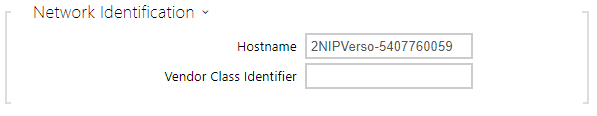
- Hostname – set the 2N IP intercom network identification.
- Vendor Class Identifier – set the vendor class identifier as a string of characters for DHCP Option 60.
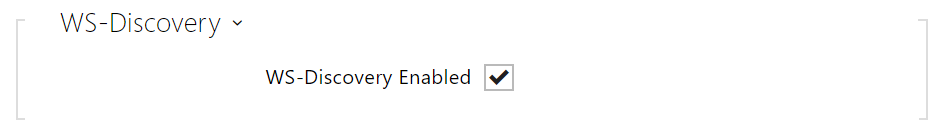
- WS-Discovery Enabled – enable the WS-Discovery function, which allows the other ONVIF clients to search a compatible device in the LAN. Enable this function to use a device as an ONVIF compatible one.
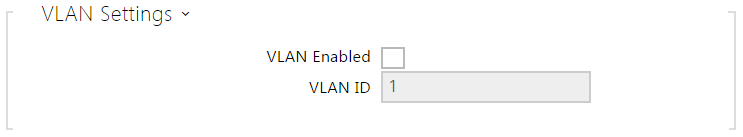
- VLAN Enabled – enable the virtual network (VLAN) support (according to recommendation 802.1q). Set the virtual network ID too to make the function work properly.
- VLAN ID – select a virtual network ID in the range of 1-4094. The device shall receive only the packets tagged with this ID. A wrong setting may result in a connection loss and need to reset the device to factory values.
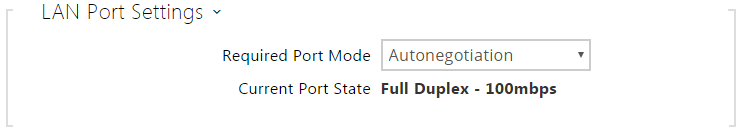
- Required Port Mode – set the preferred network interface port mode: Autonegotiation or Half Duplex – 10 mbps. The lower bit rate of 10 mbps may be necessary if the used network infrastructure (cabling) is not reliable for the 100mbps traffic.
- Current Port State – current network interface port state (Half or Full Duplex – 10 mbps or 100 mbps).
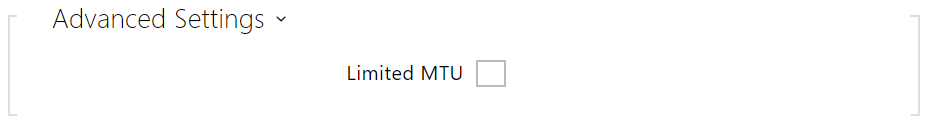
- Limited MTU – enable the shortened MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) support to make the device work properly in the networks that only support shorter MTU.
802.1x
Caution
- The authentication setting changes will not apply until the device is restarted.
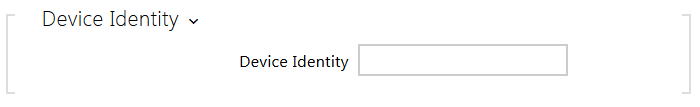
- Device Identity – username (identity) for authentication via EAP-MD5 and EAP-TLS.
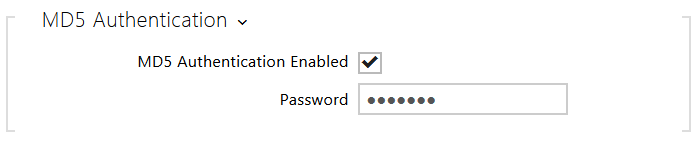
- MD5 Authentication Enabled – enable authentication of network devices via the 802.1x EAP-MD5 protocol. Do not enable this function if your LAN does not support 802.1x. If you do so, the intercom will become inaccessible.
- Password – enter the access password for EAP-MD5 authentication.
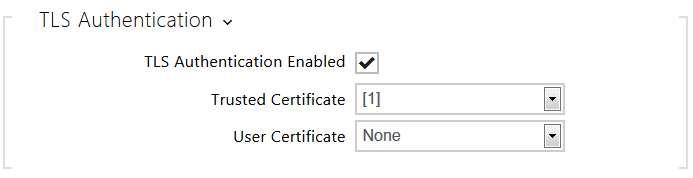
- TLS Authentication Enabled – enable authentication of network devices via the 802.1x EAP-TLS protocol. Do not enable this function if your LAN does not support 802.1x. If you do so, the intercom will become inaccessible.
- Trusted Certificate – specify the set of trusted certificates for verification of the RADIUS server public certificate validity. Choose one of three sets of certificates; refer to the Certificates subsection. If no trusted certificate is included, the RADIUS public certificate is not verified.
- User Certificate – specify the user certificate and private key for verification of the intercom authorisation to communicate via the 802.1x-secured network element port in the LAN. Choose one of three sets of user certificates and private keys; refer to the Certificates subsection.
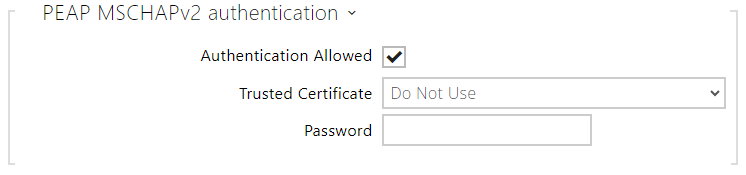
- Authentication Allowed – enable authentication of network devices via the 802.1x PEAP MSCHAPv2 protocol. Do not enable this function if your LAN does not support 802.1x. If you do so, the device will become inaccessible.
- Trusted Certificate – specify the CA certificate for verifying the RADIUS server public certificate validity. If none is available, the RADIUS server public certificate is not validated.
- Password – enter the access password for PEAP-MSCHAPv2 authentication.
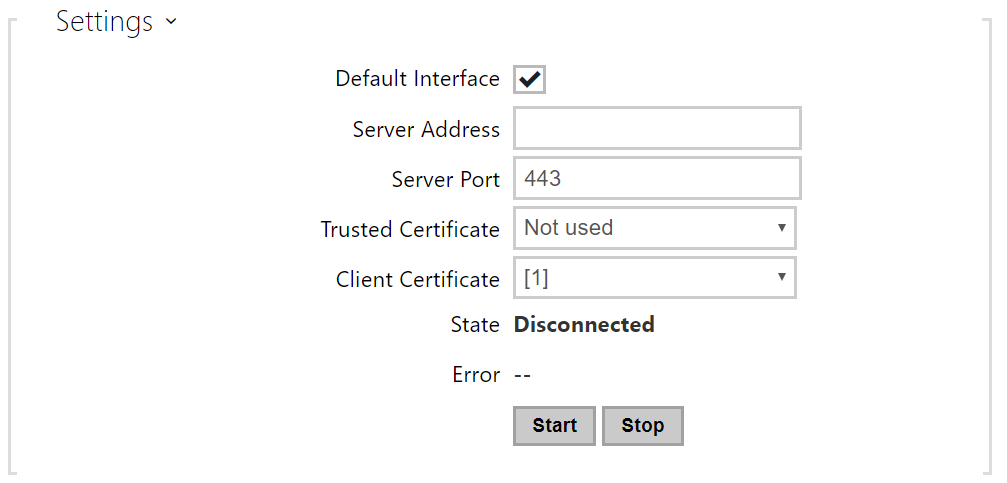
OpenVPN
Use OpenVPN to connect the device to another network.
- Enabled – enables the virtual private network (VPN).
- Default Interface – if enabled, it directs all outgoing network traffic to the VPN interface outside the LAN mask.
- Server Address – OpenVPN Server Address
- Server Port – OpenVPN Server Port.
- Trusted Certificate – specify a set of certificates issued by certification authorities to verify the OpenVPN server public certificate validity. Choose one of three certificate sets, see the Certificates subsection. If no certificate issued by a certification authority is specified, the OpenVPN server public certificate is not validated.
- Client Certificate – specify a set of client certificates to verify the client’s identity by the OpenVPN server. Choose one of three certificate sets, see the Certificates subsection. If no client certificate is specified, the OpenVPN client identity is not validated.
- State – display the OpenVPN connection state: Connected/Disconnected.
- Error – display the OpenVPN connection error type if any.
- Start – connect the device to OpenVPN.
- Stop – disconnect the device from OpenVPN.
- VPN – display the basic information on VPN.
Tip
- Refer to FAQ for OpenVPN server and client setting details.
Firewall
Tip
- Enable the firewall to protect the device against malicious requests. It is strongly recommended to have the firewall activated all the time.
- Enabled – enables the firewall.
- Status – Indicates the status of the firewall. The firewall states may be Disabled, Running or Possible Attack Detected (when a problem is detected and some requests are ignored).